- Blogs
- How Much Insulation Do I Need? A Comprehensive Guide
How Much Insulation Do I Need? A Comprehensive Guide

Insulation within your home or facility was once a low priority task that didn't really feature high in homeowners' to-do list, as what's out of sight is out of mind. Ever since utility prices have skyrocketed it is now more important than ever to make sure your building is insulated to the max to conserve that energy that you have had to pay so much to use.
High-quality insulation, when installed properly, can boost the overall energy efficiency of a building, irrespective of the heating or ventilation system you have in place.
All buildings are insulated to some degree, no matter how old they are. Over time, building regulations changed, as did the minimum requirement for insulation materials within a building. This means that, depending on when it was constructed, your building could have hardly any insulation or have levels of super insulation, such as in Passivhaus designs.
In this blog, we will be discussing some of the building regulations for loft insulation, wall insulation and others. Furthermore, we will determine how much insulation needs to be installed in these areas in order to comply with building regulations. We will also cover the various factors that influence the thickness of the insulation that you need to insulate lofts and walls.
Before we dive into the main topic, let us first understand some common values that are used to assess the insulating ability of the material:
R-value:
The R-value of the insulating material is a measurement of its ability to resist heat flow through a certain thickness. A higher R-value means greater resistance to heat flow, which means better insulating properties.
Though the R-value is the usual standard to ascertain the insulating ability of a material, it only considers heat transfer through conduction. It is also more widely used in North America than it is here in the UK. So, to get a better idea of the insulating properties, U-values are considered by building regulations.
U-value:
A U-Value estimates the quantity of heat lost through a square metre of the relevant material. It measures the capacity of an element to transfer heat from a warm space to a cold place in a structure, through all three modes of heat transfer. A lower U-Value equates to better insulation.
The U-value also measures the combined thermal resistance of all the layers that make up the particular element of the structure in question. For example in a loft conversion to calculate U-Values so you can adhere to building regs, you have to consider some or all of the following 7 components.
- The roof tiles
- Breathable membrane
- Wooden rafters
- The insulation itself
- Plasterboard
- Finished plaster skim
- Paint
Rather than gauging the effectiveness of a single material, U values calculate part of a construction's total insulating performance, such as the entirety of a wall, or the entirety of a floor makeup. Adjustments for any air gaps are also included in the U-values plus, when estimating the U-value, the average ambient temperatures within and outside a building are also considered.
Obviously of all the 7 components listed above, the insulation material and its thickness have the biggest impact on the final U-Value.
U Values are an important part of Building Regulations Approved Document Part L and Section Six of the Scottish Standards, both demand that you satisfy a particular standard of U-Value while carrying out building works.
Thermal conductivity or lambda value:
Measured in Watts per metre Kelvin (W/mK), the thermal conductivity aka the Lambda value is the estimate of how readily heat passes through a given material type, regardless of its thickness. The lower the thermal conductivity of the insulating material, the greater is its thermal performance, meaning, heat will pass through the material slower from a warm space to a colder space and vice versa.
For example, glass mineral wool loft insulation roll has a lambda value of 0.044w/mk while the value for Celotex XR4000 PIR board is 0.022w/mk which states that PIR board provides better insulation by nearly double compared to fibreglass.
Thermal Conductivity and U-Values are critical factors that influence the thickness of the insulation you need. If you need help with choosing the right type of insulation, please get in touch with us and we would be happy to help where we can. It must be stated that at the end of the day, it's best to consult with a Building Control Officer, in fact if the proposed works come under Building regs then it's indeed necessary when it comes to U-Values. They will do the proper calculations necessary which are unique to your property and tell you the type of insulation and thickness required.
Other Factors affecting Insulation thickness include
- The areas you plan to insulate in your home like lofts, floor etc
- The sort of insulation you choose.
- And of course, where you live in the world, be it hotter or colder, more humid etc.
Some pointers listed below can assist you to understand the best way to insulate your house or building to comply with the building regulations. However, before going ahead and buying insulation online or visiting your local vendor, you need to check the existing insulation in your home.
How much loft insulation do you require?
As mentioned in Approved Document L, a new build needs to have about 250- 270mm of mineral wool loft insulation in the loft, to attain the U-value of 0.11w/ m2k for new builds (and 0.16 w/ m2k for extensions). Some new buildings are even raising their loft insulation to 300mm nowadays.
Calculating how much insulation you need is the critical first stepin in insulating lofts. You will need to measure the length and width of your lofts to know the area in square metres. Knowing how many sq.m you need to cover, will give you an inclination to the number of loft insulation rolls you need.
You do not want the hassle of returning extra loft insulation rolls to the vendor or ending up paying for more rolls than necessary. The graph below depicts the number of mineral wool loft insulation rolls required on sq.m basis:
* Note: The graph above indicates a typical loft insulation roll of 170mm thickness, with a width of 1.14 metres, a length of 5.68 metres. Make sure you check the roll size before purchasing.
Also, you need to check if you have any existing insulation in your lofts. If you already have loft insulation installed and if your home is quite old, the level might be anything between 25 to 200 mm. A 25mm loft insulation was the minimum required to comply with the regulations back in the 80s which we know now to be woefully inadequate.
Ensure that you also check whether the existing insulation fills the void in between joists or whether it comes over the joist. If insulation is already between the joists, fresh loft insulation rolls can be simply laid over the existing insulation in a perpendicular fashion, to attain the necessary thickness, which is 250-270mm. Just make sure that the loft insulation already present is in proper condition and is not damaged in any way i.e compressed / damp / full of rubble and dust etc. To insulate lofts, we recommend you use Superglass loft insulation rolls or Knauf loft insulation rolls.
How much wall insulation do you need?
When calculating the amount of wall insulation you'll need, you first need to know the length and width of the area that needs to be insulated.
Cavity wall insulation:
Cavity walls are usually done whilst the actual walls are being constructed because once bricks and blocks are laid it's obviously very difficult to reach that cavity.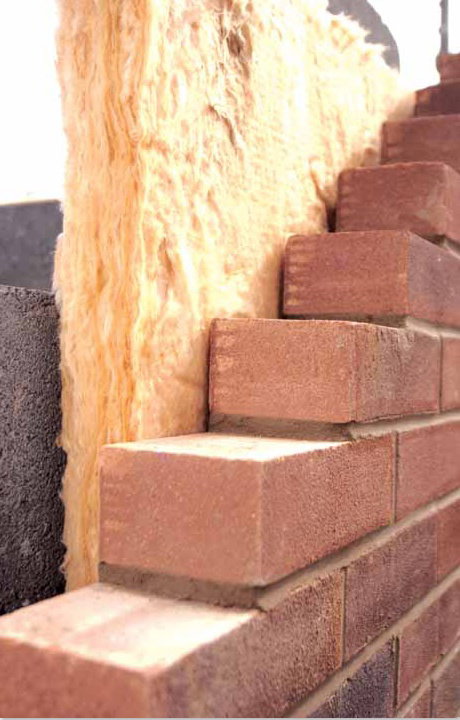
So if, for example, the cavity wall surface has a 102.5 mm block external 'layer' or wall and a medium-density blockwork internal layer, then to attain the required U-Value of 0.45 to 0.17 W/m2K (values for structures built 1995 onwards), 100-125mm of mineral wool batt insulation would be required.
If you have an existing cavity wall, check if there is any existing insulation in the cavity walls. You can do this by drilling some test holes in strategic places at multiple places along the wall, ideally at low level and out of sight, behind some furniture or something, if you are not going to get the work done straight away.
If your cavity walls aren't already filled with batt insulation, we recommend that you fill them with cavity wall insulation either using some type of blown-in insulation, insulation board or wool insulation. Obviously, this will mean you will need to gain access to the cavity or you would otherwise have to have a professional cavity wall insulation contractor come and do it for you.
External wall insulation:
Any external wall insulation when installed needs to comply with the building regulations. The required U-value for external wall insulation is 0.16 watts/m2k for new builds and 0.25 watts/m2k for extensions. Any insulating material you use needs to help achieve this value. In order to reach this value, you could make use of 90mm of Expanded Polystyrene or EPS Insulation, or 60mm insulation board, preferably something like Kingspan K5.
Any insulating material you use needs to help achieve this value. In order to reach this value, you could make use of 90mm of Expanded Polystyrene or EPS Insulation, or 60mm insulation board, preferably something like Kingspan K5.
You can also achieve the required U value using 110mm thick mineral wool insulation or 110-120mm thick wood fibre insulation. The thicker the insulating material, the better is its insulating efficiency. Closed-cell foam insulation like polystyrene insulation is totally water-resistant, which makes it a better candidate for external wall insulation in that respect but rock wool or mineral wool insulation is better for fire retardation and acoustic insulation purposes.
External wall insulation is usually a job best left to professional contractors because it's labour intensive, requires rendering in a lot of cases and is also super important to get right to prevent any kind of damp issues that might occur with a poor install.
Inner wall insulation:
One way of insulating a solid wall internally is using solid insulation boards like PIR insulation or insulated plasterboards. Another is building a stud wall on the existing solid wall and insulating it with mineral wool insulation that provides efficient thermal and acoustic insulation to the walls. Any of these should be used to help attain a U-value of 0.29-0.30 watts/m2k.
Insulated plasterboard is a great time and labour saver. Around 60mm-100mm thick insulated plasterboard, which is backed with rigid PIR insulation, is fitted to the wall surfaces which are mechanically secured using adhesives (also known as dot and dab), screws and other means.
For stud walls, a steel or wood stud wall is constructed and connected to the wall surface and is insulated between the studs using mineral wool insulation slabs or APR insulation which is short for Acoustic Partition Roll insulation. Since mineral wool insulation has a higher thermal conductivity than PIR board insulation, the thickness needs to be 120mm thick at least for the mineral wool to achieve the same effectiveness as around 60 to 70mm of PIR insulation board.
Stud wall insulation is wider and bulkier, therefore it takes up a lot more precious floor space when compared to thinner insulated plasterboards. However, stud walls are strong enough to hold the many, weighty fittings like washbasins, kitchen units and others with the right fixtures, unlike insulated plasterboards, which will require that you go all the way through insulation and into the wall behind.
Regulations for floor insulation:
Bear in mind that the U-value required varies with the floor you have and also, the kind of insulation you select. For example, a raised or suspended floor will require less insulation than a slab of concrete that is in direct contact with the substructure of the building, usually compacted hardcore or similar.
To know how much insulation you'll require to insulate your floors exactly, you’ll need to know the floor area. Measure the length and width of the floors in the room(s)that you wish to install insulation and multiply the one by the other to get the area in Square Feet / Metres. Make sure you allow at least 10% on top for waste, preferably 15%. This will give you a good idea of how many insulation board you'll need for your floors.
According to the building regulations, floor insulation needs to be a minimum of 0.25 W/2mK U-value for extension works and 0.11 W/2mK for new builds. As is most common in the UK, PIR Insulation is used in floors due it its excellent Lambda values and also compressive strength. To achieve this you will be required to use 150mm thick PIR insulation.
The table below shows the updated U-value requirements for domestic establishments in England. In mid-June 2022, the updated and revised version of Building regulations Part L will come into force in England.
|
Type of Construction |
Wall |
Floor |
Roof |
|
New Build |
0.16 |
0.11 |
0.11 |
|
Extensions- Existing Building |
0.18 |
0.18 |
0.15 |
|
Refurbishment - Existing Building |
0.3 |
0.25 |
0.16 |
The U-values have to be achieved depending on the type of insulating material, the area you are in and the type of project you want to undertake. Any good builder, insulation contractor or building control officer will assist you with the type of insulation you’d need, its thickness and the quantities required.
Pipe insulation:
There are no values or numbers that you need to follow to insulate pipes and ductwork in your home. However, you need to lag the pipes and duct systems of your home, to make it more energy-efficient and protect them from frost. Insulating both hot and cold water pipes is critical or else, you would literally be burning cash away through your boiler in the form of wasted hot water or heating for your radiators.
If you do not have much space to insulate pipes, then you may utilise a 9mm of 13mm foam pipe insulation such as nitrile rubber. These provide efficient thermal insulation and protect pipes from heat loss and freezing. Pipe insulation needs to be mechanically secured using foil tapes or duct tapes to prevent gapes, where the heat could easily escape (You can know more about insulating pipes, in our blog here). If space is not a constraint, you could use mineral wool pipe insulation that enables optimum performance.
A relatively straightforward guideline is that since bigger pipes lose heat quickly due to larger surface area, they need thicker insulation. While, for freeze protection, the smaller pipes need to be insulated with thicker lagging as tiny volume freezes quickly.
Please refer to BS5422 for up to date pipe insulation thicknesses for residential and industrial applications.
Can I have 'too much' insulation?
Technically, you can have as much insulation as you require in your home, as long as there is proper ventilation in place. But overdoing insulation may not be recommended, for the most part, because of the law of diminishing returns.
By using loft insulation as an example, upping your loft insulation from 270 mm to 400 mm isn't actually going to make as big a difference as say going from 0mm - 200mm of loft insulation, so it's worth sticking with the recommended thicknesses that strikes the right balance and return on investment.
If you are buying a brand-new home that has a higher EPC rating, you probably already have all the insulation you need. In older properties can add as much insulation as you want in the space available, but if you try to jam-pack the space too much, you might have to let go of precious storage.
Also, without proper ventilation by blocking soffit vents, for example, too much insulation could result in increased moisture levels, which could then make way for mould to rear its ugly head. So, it is advisable to stick to the regulations and ventilate your home properly.
Conclusion:
In his blog, we have looked into the minimal thickness and also, some building regulations that ensure your property is insulated to a high standard so it will be warm and snug in the winter and cool in the summer. We suggest seeking a professional to discuss the U-values and building regulations, even before you begin any kind of installation work.
For the best quality loft insulation, wall insulation and also pipe insulation, duct insulation along with things like valve jackets, don’t forget to visit Buy Insulation Online. We offer free delivery in major cities and also plant three trees per order, thus offsetting nearly a ton of your carbon!

Samuel Hitch
Managing Director
Buy Insulation Online.
Leave A Reply
Your feedback is greatly appreciated, please comment on our content below. Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *