- Blogs
- The Ultimate Guide to Insulation Values
The Ultimate Guide to Insulation Values

In the pursuit of energy efficiency and sustainable living, insulation plays a crucial role. Not only does it allow for comfortable indoors whilst saving money, but it also allows for a sustainable environment, which is the need of the hour.
This article serves as a comprehensive guide to understanding insulation values and their significance. We will explore the insulation values in detail, the factors affecting them and key considerations. We will also discuss the different insulation materials and their insulation values. By the end, you'll have significant knowledge about the different insulation types and values, so you can make an informed decision and choose the right insulation for your home.
What Are Insulation Values?
Insulation values, also known as thermal resistance values, measure the ability of an insulation material to resist heat transfer. They are crucial in determining the effectiveness of insulation in reducing heat loss or gain in a building.
Types of Insulation Values
In the United Kingdom, the insulation values primarily used to assess the thermal performance of buildings are U-values, K-values and R-values. Let's get into the details:
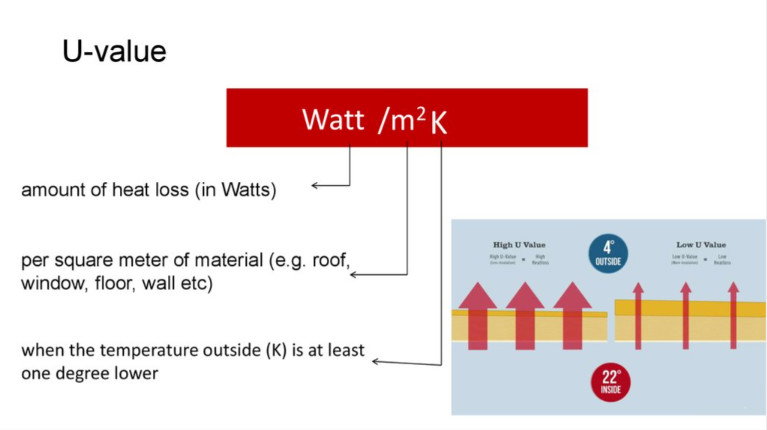
What are U Values (Thermal Transmittance): ![]()
U-value is the most commonly used insulation value in the UK. It measures the rate of heat loss or gain through a specific material or building element, such as walls, roofs, floors, and windows. U-values are expressed in units of watts per square meter per Kelvin (W/m²K). Lower U-values indicate better insulation performance, as they indicate lower heat transfer rates.
Factors affecting U values:
-
The inherent thermal conductivity of the insulation material plays a significant role in determining the U-value. Materials with lower thermal conductivity have better insulating properties and typically result in lower U-values.
-
The thickness of the insulation material affects the U-value. Increasing the thickness of the insulation generally decreases the U-value, as it provides greater resistance to heat transfer.
-
The density of the insulation material can also influence the U-value. Higher density often leads to lower U-values due to reduced air gaps within the material, which decreases heat conduction.
-
Thermal bridging occurs when there is a direct heat transfer path through elements such as studs, beams, or metal frameworks. The presence of thermal bridges can increase the U-value by providing alternate pathways for heat to escape or enter the building.
-
Installation Quality: The quality of installation is crucial for achieving the desired U-value. Gaps, compression, or improper sealing can compromise the insulation's performance, leading to higher U-values.
Key Considerations:
The UK building regulations mandate specific U-value requirements for different parts of a building, including walls - internal external and cavity insulation, roofs, floors, and windows. Compliance with these regulations ensures that the thermal performance of the building meets the minimum energy efficiency standards set by the government.
When conducting energy performance calculations and energy assessments for buildings, the U-value is a crucial parameter. By considering the U-values of various building elements, such as insulation materials in walls or roof assemblies, the overall thermal efficiency of the building can be evaluated and assessed.
When considering insulation upgrades or major refurbishments in existing buildings, the U-value serves as a benchmark to improve thermal performance. By comparing the existing U-value with the desired target U-value, homeowners and professionals can select appropriate insulation materials to achieve the desired energy efficiency improvements.
What is Thermal Conductivity or K-Value? ![]()
The K-value, also known as thermal conductivity, measures the ability of a material to conduct heat. It represents the amount of heat that passes through one square meter of a material with a thickness of one meter when there is a temperature difference of one Kelvin (1 K) between its surfaces.
In simple words, materials with high thermal conductivity like copper, allow heat to flow through them more readily, while those with low thermal conductivity slow down heat transfer. The unit of measurement for thermal conductivity is typically watts per meter Kelvin (W/mK).
The K-value of an insulation material depends primarily on its inherent thermal conductivity. The K-value represents the material's ability to conduct heat, with lower values indicating better insulation performance. Other factors such as material composition, density, and moisture content can also influence the K-value to a certain extent.
What are R Values (Thermal Resistance): ![]()
The R-value measures the thermal resistance of a material or assembly. It indicates the insulation's ability to resist heat flow. Higher R-values signify better insulation performance. R-values are expressed in units of square meter Kelvin per watt (m²K/W).
The R-value of an insulation material depends on its thermal conductivity, thickness, density, and the absence of thermal bridging. Lower thermal conductivity, greater thickness, higher density, and reduced thermal bridging contribute to higher R-values, and therefore a better insulation performance.
Insulation Values of Materials
There are many different types of insulation materials commonly used in the UK, each with its own thermal properties and insulation values.
| Insulation Material | U-Value (W/m²K) Range | R-Value (m²K/W) Range | K-Value (W/mK) Range |
| Mineral Wool (Glass Wool or Rock Wool) | 0.030 - 0.040 | 2.5 - 3.3 | 0.035 - 0.040 |
| Expanded Polystyrene foam Insulation (EPS Insulation) | 0.030 - 0.038 | 2.6 - 3.3 | 0.030 - 0.040 |
| Extruded Polystyrene foam Insulation (XPS Insulation) | 0.028 - 0.038 | 2.6 - 3.6 | 0.028 - 0.038 |
| Polyisocyanurate Insulation (PIR) and Polyurethane (PUR) Foam | 0.022 - 0.028 | 3.6 - 4.5 | 0.022 - 0.028 |
| Cellulose Insulation (Recycled Paper Fibers) | 0.036 - 0.042 | 2.4 - 2.8 | 0.036 - 0.042 |
| Reflective Foil Insulation (Multifoil) | 0.036 - 0.040 | 2.5 - 2.8 | |
| Phenolic Foam | 0.018 - 0.028 | 3.6 - 5.6 | 0.018 - 0.028 |
Insulation values for some natural fibre insulation:
| Insulation Material | R-Value (m²K/W) Range | K-Value (W/mK) Rang | U-Value (W/m²K) Range |
| Hemp Wool | 2.5 - 4.5 | 0.040 - 0.060 | 0.22 - 0.40 |
| Sheep's Wool | 3.5 - 4.5 | 0.035 - 0.045 | 0.22 - 0.29 |
| Wood Fiber Insulation | 1.5 - 3.5 | 0.040 - 0.060 | 0.18 - 0.40 |
Please note that the values provided are general ranges and may vary depending on specific product formulations, thicknesses, and applications. It's essential to consult manufacturers' specifications and relevant standards for precise values applicable to a particular insulation material and project requirements.
Building Regulations And Insulation Values:
In the United Kingdom, building regulations provide guidelines and requirements related to insulation values to ensure energy efficiency and thermal performance in buildings. Compliance with the applicable building regulations ensures that insulation values and thermal performance in buildings meet the required standards, contributing to reduced carbon emissions and improved comfort for occupants.
The specific regulations may vary slightly between England, Scotland, Wales, and Northern Ireland. Here is an overview of the building regulations relating to insulation values in the UK:
-
England: In England, the Building Regulations 2010 (Part L) covers the conservation of fuel and power. It sets requirements for thermal performance, including insulation, in new buildings and major refurbishment projects. The regulations specify maximum U-values for different building elements, such as walls, roofs, floors, and windows. Compliance with the prescribed U-values is necessary to obtain building approval.
-
Scotland: In Scotland, the Building (Scotland) Regulations 2019 (Section 6) focuses on energy and carbon dioxide emissions. The regulations outline specific U-value requirements for walls, roofs, floors, and windows. Compliance with the U-value limits is necessary for new buildings and major refurbishments to meet energy performance standards.
-
Wales: In Wales, the Building Regulations 2010 (Part L) is applicable, similar to England. It covers the conservation of fuel and power and sets out the requirements for thermal performance and energy efficiency. The regulations specify maximum U-values for various building elements to ensure compliance with energy efficiency standards.
-
Northern Ireland: In Northern Ireland, the Building Regulations (Northern Ireland) 2012 (Part F) deals with energy efficiency and thermal insulation. It sets requirements for U-values in walls, roofs, floors, and windows, aiming to achieve energy-efficient building envelopes.
Please note that these regulations are periodically updated to align with evolving energy efficiency targets and standards. It is recommended to consult the specific building regulations and relevant amendments in your region for the most up-to-date information and requirements.
Current Building Regulations for Loft Insulation:
The current recommended insulation value for loft insulation in the UK is a U-value of 0.16 W/m²K. This corresponds to a minimum insulation thickness of approximately 270mm of mineral wool insulation. These values are something you need to consider while insulating your loft to ensure energy-efficient loft spaces.
Current Building Regulations for Cavity Wall Insulation
The current insulation value required to meet building regulations for cavity wall insulation in the UK is a U-value of 0.18 W/m²K for new builds and 0.30 W/m²K for existing walls. This value ensures that cavity walls are adequately insulated to minimise heat loss and improve energy efficiency in buildings.
Frequently Asked Questions
Do insulation values vary with insulation thickness?
Yes, insulation values such as U-value and R-value can be influenced by the thickness of the insulating material. Increasing the thickness generally leads to lower U-values and higher R-values, indicating better insulation performance. The K-value, representing thermal conductivity, is typically unaffected by thickness but can vary between different insulation products.
Do insulation values vary with the density of the insulation type?
Insulation values such as U-value and R-value can be influenced by insulation density. Higher insulation density generally leads to lower U-values and higher R-values, indicating improved insulation performance. The impact on K-value may be less pronounced but can still vary depending on the specific insulation material.
What is the relationship between K value and U-value?
The K-value and U-value are directly proportional. The K-value represents the thermal conductivity of a material, indicating how well it conducts heat. The U-value, on the other hand, measures the overall heat transfer through a material or assembly. The U-value is calculated by considering the K-value, thickness, and other factors. Therefore, as the K-value decreases, the U-value decreases, indicating improved insulation efficiency.
What is the relationship between R-value and K-value?
The R-value and K-value are reciprocal. The R-value represents the thermal resistance of an insulating material, indicating its ability to slow heat flow. The K-value, on the other hand, represents the thermal conductivity of a material, indicating how well it conducts heat.
The relationship between the two is given by the equation R = thickness / K, where thickness is the thickness of the material. As the K-value decreases, the R-value increases, indicating improved insulation effectiveness. Conversely, as the K-value increases, the R-value decreases, indicating reduced insulation performance.
What is the relationship between R-value and U-value?
The R-value and U-value are inversely proportional. As the R-value increases, indicating better insulation, the U-value decreases, indicating reduced heat transfer. A higher R-value corresponds to a lower U-value, signifying improved insulation performance.
In Conclusion:
In conclusion, understanding insulation values is crucial for achieving energy efficiency and achieve comfortable living spaces, all the while reducing your carbon footprint. Insulation values such as U-value, R-value, and K-value provide insights into the thermal properties of insulation materials.
By considering insulation values, homeowners and professionals can make informed decisions when selecting materials and improving the energy efficiency of buildings. By choosing the right insulation and by installing it the right way you can easily reduce energy consumption, lower utility bills, and contribute to a more sustainable environment. We do recommend consulting local building regulations and industry standards for specific requirements in your region.
For top-rated insulation materials like insulation batts, insulation boards, multifoils and more visit Buy Insulation Online. Not only do we strive to bring you top insulation brands at the lowest possible prices, but we also plant a tree for every order thereby taking you a step closer to sustainable living.

Samuel Hitch
Managing Director
Buy Insulation Online.
Leave A Reply
Your feedback is greatly appreciated, please comment on our content below. Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *