- Blogs
- How to Improve Your Home’s Energy Efficiency with Wall Insulation
How to Improve Your Home’s Energy Efficiency with Wall Insulation

If you are looking for ways to save money on your energy bills and make your home more comfortable, one of the best things you can do is to install wall insulation. Wall insulation is a material that reduces the heat transfer between the inside and outside of your home, keeping it warmer in winter and cooler in summer. Wall insulation also helps to reduce noise, improve air quality, and prevent moisture problems.
But how do you know what type of wall insulation is best for your home? And how do you install it properly? In this article, we will answer these questions and more, and guide you through the process of choosing and installing wall insulation for energy efficiency.
Why Wall Insulation Matters
 According to the Department for Energy Security and Net Zero, about 35% of the heat loss in a typical British home happens through the walls. This means that if your walls are not properly insulated, you are wasting a lot of energy and money to heat or cool your home. By installing solid wall insulation, you can reduce this heat loss by up to 50%, depending on the type and thickness of the insulation. This can translate into significant savings on your energy bills, as well as a more comfortable and consistent indoor temperature.
According to the Department for Energy Security and Net Zero, about 35% of the heat loss in a typical British home happens through the walls. This means that if your walls are not properly insulated, you are wasting a lot of energy and money to heat or cool your home. By installing solid wall insulation, you can reduce this heat loss by up to 50%, depending on the type and thickness of the insulation. This can translate into significant savings on your energy bills, as well as a more comfortable and consistent indoor temperature.
Wall insulation also has other benefits, such as:
- Reducing noise: Wall insulation can act as a sound barrier, blocking or absorbing unwanted sounds from outside or inside your home. This can improve your privacy and peace of mind, especially if you live in a noisy area or have loud neighbours.
- Improving air quality: Wall insulation can prevent air leaks, which can cause drafts, dust, allergens, and pollutants to enter your home. By sealing your walls, you can improve the indoor air quality and reduce the risk of respiratory problems, allergies, and asthma.
- Preventing moisture problems: Wall insulation can also prevent moisture from condensing on your walls, which can lead to mould, mildew, rot, and structural damage. By keeping your walls dry, you can protect your home from these issues and maintain a healthy and safe environment.
Types of Wall Insulation
There are many types of wall insulation available, each with its advantages and disadvantages. The most common types are:
- Blanket insulation batts and rolls: This is composed of fibreglass, mineral wool, cotton, or sheep’s wool, and come in pre-cut or rolled forms designed to fit between wall studs or joists, ideal for internal wall insulation, lofts, and floors. Their advantages lie in cost-effectiveness, ease of installation, and efficient thermal and sound insulation, being widely compatible with various wall types. However, their use poses some drawbacks: potential irritation to lungs, eyes, and skin leading to health concerns, susceptibility to reduced effectiveness when wet, compressed, or damaged, and the possibility of allowing heat conduction through the wall's structural elements.
- Foam board insulation: This is a rigid board of polystyrene, polyisocyanurate, or polyurethane foam, which can be attached to the outside or inside of wall surfaces. It provides a high R-value per inch of thickness, and it can also act as a vapour barrier and air seal. However, it is more expensive and difficult to install than blanket insulation, and it may require additional fire protection.
- Loose-fill insulation: This is a material that can be blown or poured into wall cavities, such as cellulose, fibreglass, or mineral wool. It is ideal for filling irregular spaces and gaps, and it can provide good thermal and sound insulation. However, it may settle over time and lose some of its effectiveness, and it may require professional installation and special equipment.
- Spray foam insulation: This is a liquid foam that expands and hardens when sprayed into wall cavities, such as polyurethane, icynene, or cementitious foam. It provides excellent thermal and sound insulation, as well as air sealing and moisture control. However, it is the most expensive and complex type of insulation, requiring professional installation and careful handling.
Understanding Cavity Wall Insulation
Cavity Wall Insulation: Enhancing Energy Efficiency
Cavity walls, consisting of two layers with a gap in between, often result in heat loss. Addressing this through cavity wall insulation is an effective way to reduce energy consumption and lower heating bills. By filling the gap with insulation material, this process reduces the amount of heat lost and improves the thermal performance of your home.
Energy Savings and Home Improvements
Installing cavity wall insulation contributes significantly to energy savings. It helps reduce heat loss, especially in homes built before the 1920s that might lack insulation. This insulation will help insulate solid walls and prevent heat from escaping an uninsulated home. This measure is essential to consider for greater energy efficiency and to cut your heating costs.
External and Internal Insulation: A Comprehensive Approach
External wall insulation involves weatherproofing the outside walls with insulation boards, while internal insulation adds insulation to the inside. Both methods improve the energy efficiency of a home, reducing carbon emissions and lowering heating bills.
Importance of Professional Installers and Building Regulations
For effective cavity wall insulation, employing qualified installers is crucial. Compliance with building regulations ensures proper insulation installation and helps improve the living environment while conserving energy. It's important to check with local authorities before carrying out insulation work.
Challenges and Solutions: Uninsulated Homes and Retrofitting
Uninsulated homes suffer from heat loss, causing higher energy consumption and carbon emissions. Retrofitting such homes with cavity wall insulation, along with loft insulation, is a recommended approach to improve energy performance. However, homes without a cavity may require alternative methods, such as insulating the walls from the outside or inside to reduce heat loss and enhance energy efficiency.
How to Choose the Right Wall Insulation for Your Home
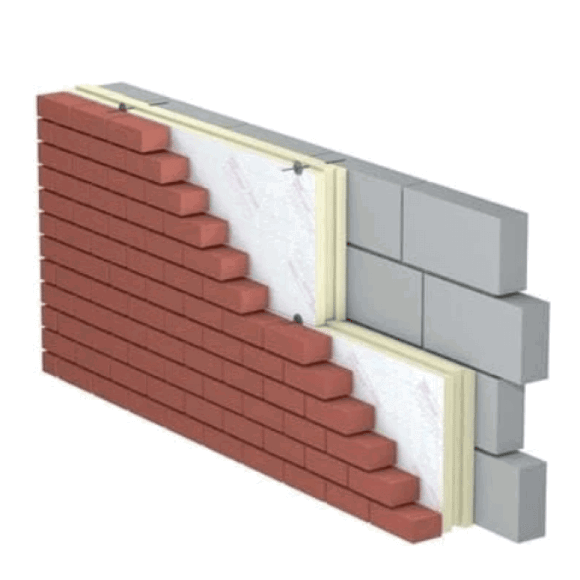 The type of wall insulation that is best for your home depends on several factors, such as:
The type of wall insulation that is best for your home depends on several factors, such as:
- The climate and location of your home: Different climates require different levels of insulation to achieve optimal energy efficiency. The Department for Energy Security and Net Zero provides a map that shows the recommended U-values for different regions and areas of your home. The U-value is a measure of how much heat is lost through a material, and the lower the U-value, the better the insulation. For example, if you live in a cold climate, you may need a lower U-value for your walls than if you live in a warm climate.
- The age and construction of your home: Older homes tend to have less insulation than newer homes, and they may have different types of walls and framing. For example, if you have a brick or stone wall, you may need a different type of insulation than if you have a wood or metal wall. You may also need to consider the existing insulation, if any, and whether you need to remove or supplement it.
- The cost and availability of the insulation: The cost of insulation varies depending on the type, thickness, and quality of the material, as well as the labour and equipment required for installation. You may also need to consider the availability of the insulation in your area, and whether you can find a reliable and qualified contractor to install it. You may want to compare the initial cost of the insulation with the potential savings on your energy bills over time and choose the option that gives you the best value for money.
How to Install Wall Insulation Properly
The installation of wall insulation is a critical step in improving your home’s energy efficiency, and it should be done with care and precision. The installation method depends on the type of insulation and the type of wall, but some general guidelines apply to all cases, such as:
- Follow the manufacturer’s instructions and safety precautions carefully, and check the local building and fire codes before you start.
- Prepare the wall surface by removing any obstacles, such as electrical boxes, pipes, wires, or nails, and repairing any holes or cracks. You may also need to install a vapour barrier or a house wrap to prevent moisture problems.
- Cut and fit the insulation to the wall cavity, making sure that there are no gaps or overlaps. You may need to use a utility knife, a tape measure, a straight edge, and a stapler to do this. You may also need to use a blower, a hose, or a spray gun to fill the wall cavity with loose-fill or spray foam insulation.
- Secure the insulation to the wall surface, using nails, screws, adhesives, or clips, depending on the type of insulation and the type of wall. You may also need to use a caulk gun or a foam gun to seal any air leaks around the edges of the insulation.
- Cover the insulation with a suitable finish, such as drywall, plaster, or siding, and apply the appropriate paint or coating. You may also need to install electrical outlets, switches, or fixtures on the wall surface.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: How does wall insulation help improve energy efficiency?
A: Wall insulation helps improve energy efficiency by reducing heat loss, keeping the home warm in the winter, and reducing the need for excessive heating, thus saving energy and reducing energy bills.
Q: Can wall insulation help with weatherproofing a home?
A: Yes, wall insulation can help weatherproof a home by providing a barrier against external elements, preventing heat loss, and reducing the risk of condensation, thus ensuring the home remains comfortable and dry.
Q: What are the considerations for insulating solid walls in older homes?
A: Insulating solid walls in older homes may require careful assessment of the building structure, potential issues with condensation, and the best methods for installation without compromising the architectural integrity of the property.
Q: How can I check if my home needs solid wall insulation?
A: It’s important to consider factors such as when the home was built, the type of walls it has, and the current energy performance to determine if the walls need insulation to improve energy efficiency and reduce energy use.
Q: Can installing solid wall insulation reduce energy bills?
A: Yes, installing solid wall insulation can help reduce energy bills by improving the energy efficiency of a home, reducing the need for excessive heating, and creating a more comfortable living environment, thus saving energy and money.
Conclusion
Wall insulation is one of the most effective ways to improve your home’s energy efficiency and comfort, as well as to reduce your environmental impact and save money on your energy bills. By choosing the right type of wall insulation for your home, and installing it properly, you can enjoy the benefits of a well-insulated home for years to come.
If you need more information or advice on wall insulation, you can visit our website Buy Insulation Online, where you can find a wide range of insulation products, tools, and accessories, as well as helpful guides and tips on how to insulate your home. You can also contact us for any questions or queries, and we will be happy to assist you. Thank you for reading this article, and we hope you found it useful and informative.

Samuel Hitch
Managing Director
Buy Insulation Online.
Leave A Reply
Your feedback is greatly appreciated, please comment on our content below. Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *











































































































































































































































































































































































