- Blogs
- What issues can arise with insulation? Typical issues and their remedies.
What issues can arise with insulation? Typical issues and their remedies.

Insulation is a crucial element in homes and buildings, playing a pivotal role in maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures, reducing energy consumption, and preventing moisture-related problems.
However, when insulation is improperly installed or maintained, it can lead to a range of issues that affect a building's performance, comfort, and occupants' health.
This article explores common insulation problems and their solutions, as well as eco-friendly insulation options for a more sustainable approach to insulation.
What does poor insulation look like?
Bad insulation can have different signs depending on the type, location, and condition of the insulation. Some indicators of bad insulation are:
Typical Insulation issues and their remedies.
1. High Energy Bills:
Problem: Elevated heating or cooling costs may suggest ineffective insulation, allowing excessive heat transfer into or out of your building.
Solution: Improve insulation by adding or replacing it in areas with inadequate coverage and consider upgrading to higher R-value insulation materials for better thermal resistance.
2. Uneven Temperatures:
Problem: Noticeable temperature variations between rooms or areas can signify insulation that is either unevenly distributed, damaged, or missing.
Solution: Assess insulation quality, redistribute or add insulation as needed, and seal any gaps or leaks around doors, windows, and vents to create a more consistent indoor climate.
3. Drafts:
Problem: Drafts originating from gaps around windows, doors, electrical outlets, or vents can indicate poor sealing and insulation, leading to air leakage.
Solution: Seal gaps and cracks with caulk, weatherstripping, or spray foam to prevent air leakage and improve the overall effectiveness of your insulation.
4. Mould or Mildew:
Problem: The presence of mould or mildew on walls, ceilings, floors, or insulation is often a result of damp or wet insulation, creating favourable conditions for fungal growth.
Solution: Address moisture issues by fixing leaks or improving ventilation, replace damaged insulation, and consider using mould-resistant insulation materials.
5. Pest Infestation:
Problem: The appearance or sounds of rodents, insects, or birds within walls, attics, or crawl spaces may be attributed to insulation that provides shelter and food sources for pests.
Solution: Repair any entry points that pests are using to access your home, replace damaged insulation, and consider pest-proofing measures like installing screens or mesh barriers.
6. Ice Dams:
Problem: The formation of icicles on roof edges or water leaks in the attic or ceiling can be caused by inadequate insulation, allowing heat loss from the roof and subsequent snow melting and refreezing.
Solution: Improve attic insulation and ventilation to maintain consistent temperatures on the roof, preventing snowmelt and ice dam formation. Properly insulate and air-seal attic access points as well.
7. Condensation:
Problem: Condensation occurs when warm, moist air meets cold surfaces due to inadequate insulation, potentially leading to mould growth, health issues, and structural damage.
Solution: Properly insulate walls and HVAC components, maintain adequate ventilation, and control indoor humidity levels to prevent condensation.
8. Air Leakage:
Problem: Air leakage occurs when unconditioned air enters or conditioned air escapes through gaps and cracks, reducing insulation effectiveness and causing discomfort.
Solution: Seal gaps with caulk, weatherstripping, or spray foam, and augment insulation in areas like the attic, basement, and crawl spaces for an improved thermal barrier.
9. Cold Floors and Walls:
Problem: Cold floors and walls indicate uneven or insufficient insulation, causing discomfort and increased energy consumption.
Solution: Assess insulation quality in walls and floors, add more insulation as needed, and consider radiant heating systems or area rugs for added warmth.
10. Mystery Odours:
Problem: Unpleasant odours stemming from insulation can result from various issues, including mould, animal infestations, chemical off-gassing, or water damage.
Solution: Identify and remove odour sources, replace damaged insulation, and enhance indoor air quality through fans, filters, or dehumidifiers.
11. Allergic Reactions:
Problem: Allergens or irritants within insulation can trigger allergic reactions like sneezing, coughing, itching, rashes, or asthma attacks.
Solution: Choose non-toxic insulation materials, maintain clean and dry conditions to prevent mould and pests, and consider air purification measures.
Addressing these insulation problems and implementing the corresponding solutions can greatly improve the comfort, energy efficiency, and safety of your living or working space.
The unseen implications of ageing on your insulation
Insulation materials can deteriorate over time due to various factors, such as exposure to moisture, sunlight, temperature changes, mechanical stress, chemical reactions, biological agents, and fire.
The ageing process can affect the physical properties, thermal performance, and durability of the insulation. Depending on the type and quality of the insulation material, the ageing process can be slow or fast, reversible, or irreversible, and uniform or non-uniform.
Some of the effects of ageing on insulation are:
- Loss of R-value: The R-value is a measure of how well an insulation material resists heat flow. The higher the R-value, the better the insulation. However, some insulation materials can lose their R-value over time due to factors such as moisture absorption, gas diffusion, compaction, cracking, or delamination.
- Loss of thickness: The thickness of an insulation material affects its R-value and coverage area. Some insulation materials can lose their thickness over time due to factors such as compression, shrinkage, settling, or erosion.
- Loss of integrity: The integrity of an insulation material refers to its ability to maintain its shape and structure under various conditions. Some insulation materials can lose their integrity over time due to factors such as deformation, distortion, fragmentation, or disintegration.
Mineral Wool
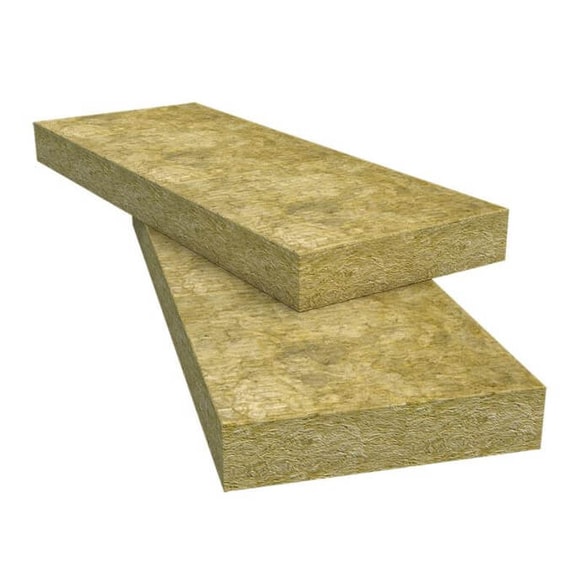 Mineral Wool is a type of fibrous insulation made from natural or synthetic minerals such as basalt, slag, glass, or rock. Mineral wool comes in different forms such as batts, rolls, loose-fill, boards, or blankets.
Mineral Wool is a type of fibrous insulation made from natural or synthetic minerals such as basalt, slag, glass, or rock. Mineral wool comes in different forms such as batts, rolls, loose-fill, boards, or blankets.
What problems can arise with Mineral Wool?
Despite its benefits, mineral wool also has some drawbacks and potential problems after installation such as:
- If the mineral wool is exposed to moisture, it can lose some of its insulating properties and become a breeding ground for mould and mildew.
- If the mineral wool is not properly installed or sealed, it can release tiny fibres into the air that can irritate the eyes, skin, and respiratory system of the occupants. Some studies have suggested that these fibres may also cause lung disease or cancer in the long term.
- If the mineral wool is damaged by rodents, insects, or birds, it can create holes or gaps in the insulation that can reduce its effectiveness and allow air infiltration.
To prevent these problems, it is important to choose high-quality mineral wool products that are resistant to moisture and fire and to follow the manufacturer's instructions for installation and maintenance.
It is also advisable to wear protective gear when handling mineral wool and to dispose of any waste material properly.
EPS Expanded Polystyrene
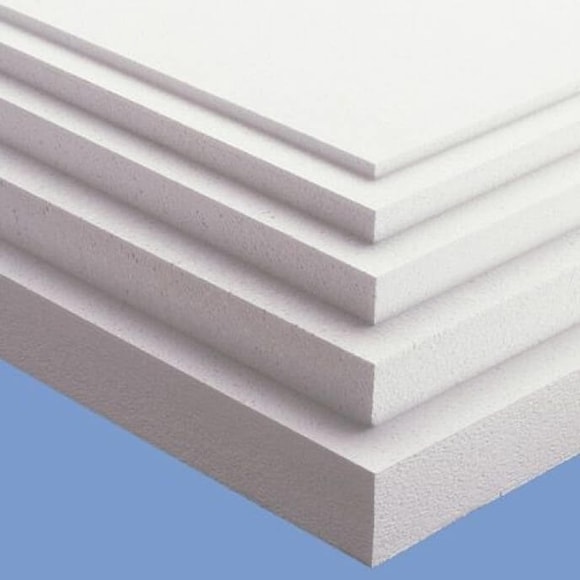 EPS expanded polystyrene is a type of rigid foam insulation made from expanded beads of polystyrene. EPS comes in different forms, such as boards, blocks, or moulded shapes. EPS has many advantages such as low cost, high R-value per inch (about R-4), lightweight, easy to cut and install, and moisture resistance.
EPS expanded polystyrene is a type of rigid foam insulation made from expanded beads of polystyrene. EPS comes in different forms, such as boards, blocks, or moulded shapes. EPS has many advantages such as low cost, high R-value per inch (about R-4), lightweight, easy to cut and install, and moisture resistance.
What problems can arise with EPS Polystyrene?
Despite its benefits, EPS also has some drawbacks and potential problems after installation such as:
- EPS polystyrene is not resistant to organic solvents, which can degrade its structure and performance.
- EPS polystyrene can release styrene, a toxic chemical, into the environment, especially when exposed to heat or sunlight. Styrene can cause health problems for humans and animals, such as irritation, fatigue, headache, depression, hearing loss, and cancer.
- EPS polystyrene is a major source of plastic pollution in the ocean, as it can break down into small pieces that are ingested by marine life or accumulate on the shorelines. EPS polystyrene can also absorb and transport other pollutants, such as pesticides and heavy metals, that harm the aquatic ecosystem.
XPS Extruded Polystyrene
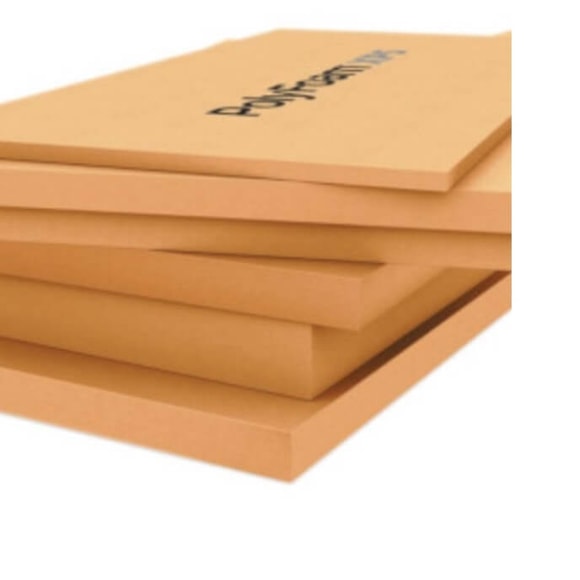 XPS extruded polystyrene is a type of rigid foam insulation made from extruded polystyrene. XPS comes in different forms such as boards, panels, or sheets. XPS has many advantages such as a high R-value per inch (about R-5), high compressive strength, low moisture absorption, and high durability.
XPS extruded polystyrene is a type of rigid foam insulation made from extruded polystyrene. XPS comes in different forms such as boards, panels, or sheets. XPS has many advantages such as a high R-value per inch (about R-5), high compressive strength, low moisture absorption, and high durability.
What problems can arise with XPS Polystyrene?
Despite its benefits, XPS also has some drawbacks and potential problems after installation such as:
- XPS is vulnerable to UV exposure, which can degrade its surface and reduce its insulation value. It is recommended to use an opaque protective covering during outdoor storage or application.
- XPS can release styrene, a toxic chemical, into the environment, especially when exposed to heat or sunlight. Styrene can cause health problems for humans and animals, such as irritation, fatigue, headache, depression, hearing loss, and cancer.
- XPS has a higher global warming potential than some other insulation materials, due to the blowing agents used in its manufacturing process. It also has limited recyclability, due to its closed-cell structure and lack of markets for recycled XPS.
- XPS is not resistant to organic solvents, which can degrade its structure and performance. It is important to avoid contact with solvent-based materials when working with XPS.
PIR Rigid Insulation
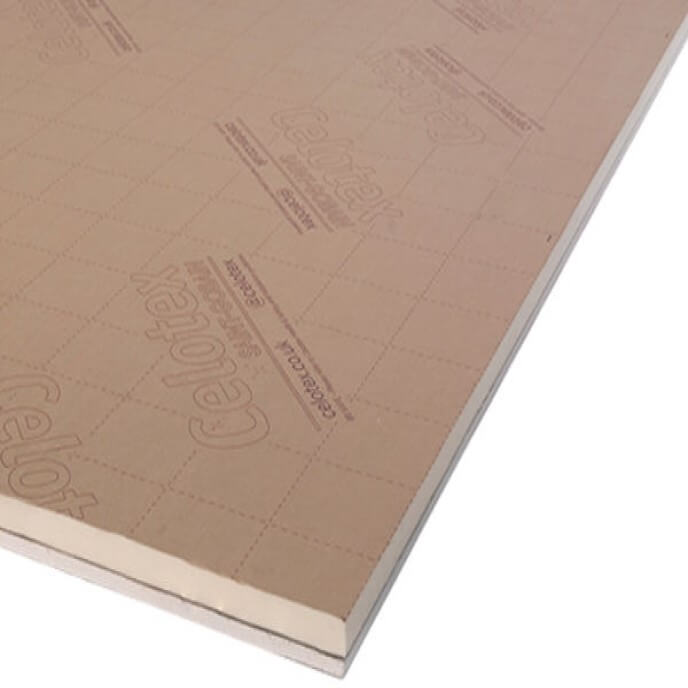 PIR rigid insulation is a type of rigid foam insulation made from polyisocyanurate. PIR comes in different forms such as boards, panels, or sheets. PIR has many advantages such as high R-value per inch (about R-6), fire resistance, moisture resistance, and dimensional stability.
PIR rigid insulation is a type of rigid foam insulation made from polyisocyanurate. PIR comes in different forms such as boards, panels, or sheets. PIR has many advantages such as high R-value per inch (about R-6), fire resistance, moisture resistance, and dimensional stability.
What problems can arise with PIR Rigid Insulation?
Despite its benefits, PIR also has some drawbacks and potential problems after installation such as:
- PIR insulation board can be a mechanical irritant to skin, eyes, and upper respiratory system during fabrication (such as dust). No statistically significant increased risks of respiratory diseases have been found in studies.
- PIR insulation boards can release toxic gases, such as hydrogen cyanide and carbon monoxide when exposed to fire. These gases can pose a serious threat to human health and safety. Therefore, the PIR insulation board should be covered by a fire-resistant material, such as plasterboard or metal cladding.
- PIR insulation board can deteriorate over time if it is exposed to high temperatures, moisture, or UV radiation. This can reduce its thermal performance and structural integrity. Therefore, the PIR insulation board should be protected from these factors by using appropriate facings, coverings, and sealants.
Phenolic Insulation Boards
 Phenolic insulation boards are a type of rigid foam insulation made from phenolic resin. Phenolic insulation boards come in different forms such as boards, panels, or sheets. Phenolic insulation boards have many advantages such as high R-value per inch (about R-7), fire resistance, sound absorption, and low smoke emission.
Phenolic insulation boards are a type of rigid foam insulation made from phenolic resin. Phenolic insulation boards come in different forms such as boards, panels, or sheets. Phenolic insulation boards have many advantages such as high R-value per inch (about R-7), fire resistance, sound absorption, and low smoke emission.
What problems can arise with Phenolic Boards?
Despite its benefits, phenolic boards also have some drawbacks and potential problems after installation such as:
- Phenolic insulation boards can shrink after curing, which can cause significant air leakage and heat transfer. This can reduce the thermal performance and energy efficiency of the insulation. Therefore, the foam insulation may need to be reapplied to the treated areas once the initial material has been set.
- Phenolic insulation boards can cause severe corrosion of metal roof decks or fasteners, which can lead to serious structural weaknesses. This is due to the acidic nature of the phenolic foam, which has a low pH value. The corrosion can also increase the heat gain of the insulation system, as the metal surface becomes rougher and less reflective.
- Phenolic insulation boards can release toxic gases, such as formaldehyde and hydrogen cyanide, into the environment, especially when exposed to fire. These gases can pose a serious threat to human health and safety, as they can cause irritation, fatigue, headache, depression, hearing loss, and cancer. Therefore, phenolic insulation boards should be covered by a fire-resistant material, such as plasterboard or metal cladding.
- Phenolic insulation boards can deteriorate over time if they are exposed to moisture, sunlight, or high temperatures. This can reduce their thermal performance and structural integrity. Therefore, phenolic insulation boards should be protected from these factors by using appropriate facings, coverings, and sealants.
What to consider when choosing insulation material?
Choosing the right insulation material for your building project can be a challenging task, as there are many factors to consider such as:
Thermal performance:
The thermal performance of an insulation material is measured by its R-value, which indicates how well it resists heat flow. The higher the R-value, the better the insulation. However, the R-value of an insulation material can vary depending on its thickness, density, ageing, and installation quality.
Therefore, it is important to compare the R-values of different insulation materials at the same thickness and conditions.
Cost:
The cost of an insulation material can include the initial purchase price, the installation cost, and the maintenance cost. The cost of an insulation material can vary depending on its availability, quality, quantity, and complexity of installation.
Therefore, it is important to compare the costs of different insulation materials over their lifespan and consider their return on investment.
Durability:
The durability of an insulation material refers to its ability to withstand various environmental and mechanical stresses such as moisture, temperature changes, fire, UV radiation, pests, or impacts.
The durability of an insulation material can affect its R-value and lifespan. Therefore, it is important to choose an insulation material that is suitable for the specific application and location of your building project.
Health and safety:
The health and safety of an insulation material refers to its potential impacts on the health and safety of the building occupants and workers. Some insulation materials can pose health and safety risks such as irritation, allergy, infection, or toxicity due to their composition, emission, or exposure.
Therefore, it is important to choose an insulation material that is safe and non-toxic for you and your family and to follow proper installation and disposal procedures.
What are some eco-friendly insulation options?
Some eco-friendly insulation options are:
- Aerogel: Aerogel is a lightweight and porous material that has a very high R-value (up to 10.3 per inch) and can block heat, sound, and moisture. Aerogel is one of the most expensive insulation options, but it can save a lot of space and energy in the long run.
- Cork: Cork is a natural and renewable material that comes from the bark of cork oak trees. Cork is also biodegradable and recyclable, making it a very eco-friendly choice.
- Icynene: Icynene is a type of spray foam insulation that is made from castor oil or other plant-based materials. Icynene is also water-based and does not contain any harmful chemicals or gases.
- Sheep’s wool: Sheep’s wool is a natural and renewable material that comes from sheep’s fleece. Sheep’s wool has a high R-value (about 3.5 per inch) and can absorb and release moisture without losing its thermal properties. Sheep’s wool is also biodegradable and compostable, making it a very eco-friendly option.
- Denim: Denim is a type of cotton insulation that is made from recycled jeans or other denim fabrics. Denim has a moderate R-value (about 3.4 per inch) and can resist mould, pests, and fire. Denim is also soft and easy to install, making it a comfortable and convenient choice.
- Cellulose: Cellulose is a type of loose-fill insulation that is made from recycled paper or wood fibres. Cellulose has a high R-value (about 3.8 per inch) and can block air leakage, sound, and fire. Cellulose is also treated with borates or other additives to prevent mould, insects, and rodents.
- Mycelium: Mycelium is a type of organic insulation that is made from the roots of mushrooms. Mycelium has a low R-value (about 2.7 per inch) but can grow to fit any shape or size of the building structure. Mycelium is also biodegradable and compostable, making it a very eco-friendly option.
- Fiberglass: Fiberglass is a type of fibrous insulation that is made from glass fibres. Fiberglass has a moderate R-value (about 2.9 per inch) and can resist fire, sound, and moisture. Fiberglass is also made from recycled glass and can be recycled again after use.
- Hemp wool: Hemp wool is made from natural and renewable hemp fibres, which are grown without pesticides or herbicides. Hemp wool has a high thermal performance and can help reduce heating and cooling costs. It also has a high sound absorption capacity, which can improve the acoustic comfort of a building.
These are some of the eco-friendly insulation options that you can consider for your home or building project. They have different advantages and disadvantages in terms of cost, performance, durability, health, and environmental impact. You should choose the one that best suits your needs and preferences.
Frequently Asked Questions
Q: What are some common issues that can arise with insulation?
A: Some common issues that can arise with insulation include wall insulation problems, cavity wall insulation problems, and internal insulation problems.
Q: What are some common problems associated with wall insulation?
A: Some common problems associated with wall insulation include penetration of moisture through the walls, homes with cavity walls that have insulation installed may experience damp problems, and the insulation may be installed incorrectly or unsuitably.
Q: What are the different types of insulation?
A: The different types of insulation include cavity wall insulation, external wall insulation, internal wall insulation, and roof insulation.
Q: What is cavity wall insulation?
A: Cavity wall insulation is a type of insulation that is installed in the gap between the external and internal walls of a house.
Q: What is an installer?
A: An installer is a professional who specializes in the installation of insulation products.
Q: How can insulation help with common problems?
A: Insulation can help address common problems such as heat loss, condensation, and energy inefficiency in homes.
Q: What is the Cavity Insulation Guarantee Agency (CIGA)?
A: The Cavity Insulation Guarantee Agency (CIGA) is an independent organization that provides guarantees for cavity wall insulation installations carried out by registered installers.
Q: What are some common problems associated with cavity wall insulation?
A: Some common problems associated with cavity wall insulation include the insulation being installed incorrectly, the insulation being unsuitable for the property, and the insulation causing damp issues.
Q: What is external wall insulation?
A: External wall insulation is a type of insulation that is applied to the exterior walls of a building.
Q: What is internal wall insulation?
A: Internal wall insulation is a type of insulation that is installed on the inside of external walls to improve thermal performance.
Conclusion:
Insulation is essential for maintaining indoor comfort and energy efficiency, but it can lead to problems if not correctly installed or maintained. Being aware of these common issues and their solutions can help improve the performance, comfort, and health of your home or building.
Additionally, eco-friendly insulation options provide sustainable alternatives for a more environmentally conscious approach to insulation.

Samuel Hitch
Managing Director
Buy Insulation Online.
Leave A Reply
Your feedback is greatly appreciated, please comment on our content below. Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *










































































































































































































































































































































































