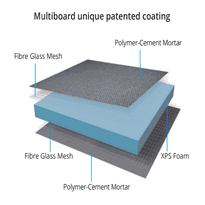
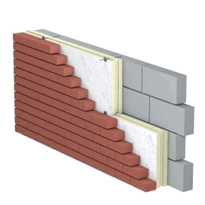
Insulation Boards
Leading brands such as Kingspan, Celotex, and Ecotherm offer rigid PIR insulation boards in multiple thickness options, including the popular 100mm Celotex, to suit different applications. From wall insulation boards to flat roof and loft insulation, these high-quality products provide durable solutions that help insulate your property effectively. PIR insulation boards made from polyisocyanurate are particularly valued for their lightweight yet high-performance properties, ensuring long-term protection against heat loss and condensation.
Explore our extensive range of insulation boards, including 100mm options, to find the perfect solution for cavity wall insulation, roof insulation, and more. Whether you’re working on a new build or retrofitting an existing structure, our insulation products will help you achieve superior thermal insulation and energy efficiency
Similar Categories

Insulation plays a crucial role in maintaining comfortable living conditions and maximizing energy efficiency in homes. By reducing heat transfer and preventing drafts, insulation helps to regulate indoor temperatures and minimize energy wastage. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore different types of insulation, various insulation materials, and the applications of insulation boards.
What is insulation and why is it important? Insulation: Explained
Insulation refers to materials used to reduce heat transfer between spaces by providing resistance to thermal flow. It is commonly installed in areas such as roofs, walls, floors, and pipes to improve energy efficiency and thermal comfort. Insulation works by trapping air pockets or using materials with low thermal conductivity, thus preventing heat from escaping or entering a building.
The Importance of Insulation in Homes
Proper insulation is essential for maintaining comfortable indoor temperatures regardless of external weather conditions. It helps minimize heat loss during winter and prevents heat gain during summer, reducing the need for excessive heating or cooling. Insulation also plays a significant role in soundproofing, reducing noise transmission between different areas of a building.
Benefits of Proper Insulation
Installing insulation in your home brings numerous benefits. Firstly, it improves energy efficiency, leading to reduced energy consumption and lower utility bills. Insulation also enhances thermal comfort by maintaining consistent indoor temperatures. Additionally, proper insulation contributes to a quieter and more peaceful living environment by minimizing noise from outside. Lastly, insulation helps to reduce the carbon footprint of a building by lowering the energy required for heating and cooling.
Types of Insulation Understanding Different Types of Insulation
Various types of insulation are available on the market, each with its advantages and drawbacks. The most common types include batt insulation, blown-in or loose-fill insulation, rigid foam insulation, and spray foam insulation. Each type differs in terms of installation method, thermal performance, and suitability for different areas of the house.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Different Insulation Types
Batt insulation, which consists of flexible fiberglass or mineral wool blankets, is cost-effective and relatively easy to install. However, it may not be the best option for uneven or hard-to-reach areas. Blown-in insulation, on the other hand, is ideal for filling irregular spaces and attics. Rigid foam insulation offers excellent thermal resistance and moisture resistance, but it requires more specialized installation. Spray foam insulation provides a seamless and airtight barrier, ensuring optimal insulation performance.
Choosing the Best Type of Insulation for Your Home
The choice of insulation depends on several factors, including the location, the desired level of thermal performance, and the specific requirements of the building. It is essential to consult with professionals or insulation experts to determine the most suitable type of insulation for your home. Taking into consideration factors such as R-value, thermal conductivity, and ease of installation will help you make an informed decision.
Insulation Materials Commonly Used Insulation Materials
Insulation materials can vary greatly, with each having unique properties and applications. Some commonly used insulation materials include fiberglass, mineral wool, polystyrene, cellulose, and polyurethane foam. These materials are chosen based on their thermal resistance, durability, ease of installation, and cost-effectiveness.
Comparing the Thermal Properties of Insulation Materials
Thermal conductivity is a crucial factor to consider when comparing insulation materials. It indicates the rate at which heat can pass through a material. Insulation materials with lower thermal conductivity are more effective in reducing heat transfer. For example, materials such as polystyrene and polyurethane foam offer high thermal resistance, making them efficient choices for insulation projects.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Different Insulation Materials
Each insulation material has its pros and cons. Fiberglass is widely used due to its affordability and excellent thermal properties. However, it can be irritating to the skin and respiratory system during installation. Mineral wool is fire-resistant, but it may sag over time. Polystyrene provides good insulation and moisture resistance, but it is not environmentally friendly. Understanding the advantages and limitations of different materials will help you make an informed decision when selecting insulation for your home.
Insulation Boards: An Overview What Are Insulation Boards?
Insulation boards are rigid panels made from various materials, such as foam, mineral wool, or fiberglass, that are used to insulate different areas of a building. These boards offer excellent thermal performance, durability, and ease of installation.
Types of Insulation Boards
There are different types of insulation boards available, including foam board insulation, polystyrene insulation boards, polyisocyanurate (PIR) insulation boards, and extruded polystyrene (XPS) insulation boards. Each type has its unique characteristics and is suitable for specific applications.
Benefits and Applications of Insulation Boards
Insulation boards provide superior thermal resistance, allowing for efficient energy savings. They are commonly used in applications such as roof insulation, floor insulation, cavity wall insulation, and flat roof insulation. Insulation boards are also ideal for insulating pipes, as they help prevent heat loss and increase energy efficiency.
Home Insulation Boards
 Home insulation plays a crucial role in maintaining a comfortable living environment and reducing energy consumption. It involves installing materials that prevent heat transfer between the interior and exterior of a home, keeping it warm in winter and cool in summer. In this ultimate guide, we will explore the different types of home insulation boards, the materials used, and their wide range of applications.
Home insulation plays a crucial role in maintaining a comfortable living environment and reducing energy consumption. It involves installing materials that prevent heat transfer between the interior and exterior of a home, keeping it warm in winter and cool in summer. In this ultimate guide, we will explore the different types of home insulation boards, the materials used, and their wide range of applications.
What is Home Insulation and Why is it Important? Definition of home insulation
Home insulation refers to the process of using various materials to create a thermal barrier that prevents heat flow between the interior and exterior of a building. It is typically installed in walls, ceilings, roofs, and floors to improve energy efficiency and provide thermal comfort.
The importance of home insulation
Home insulation is important because it helps reduce energy consumption by minimizing heat transfer, leading to significant cost savings on heating and cooling bills. It enhances the comfort level inside a home by maintaining a consistent temperature throughout the year. Additionally, it contributes to noise reduction, provides fire resistance, and improves the overall durability of a building.
How home insulation works
Home insulation works by slowing down the transfer of heat through the building envelope. Insulation materials have low thermal conductivity, which means they are poor conductors of heat. They trap air in small pockets, creating a barrier that prevents heat from escaping in cold weather and entering in warm weather. The thicker the insulation, the higher its resistance to heat flow.
Types of Home Insulation Boards Overview of different types of insulation materials
There are many different types of insulation materials available, including mineral wool insulation, rigid foam insulation, polystyrene insulation, and polyisocyanurate (PIR) insulation. Each material has its own unique properties and benefits, making it suitable for specific applications.
Advantages of using insulation boards
Insulation boards offer several advantages over other forms of insulation. They are generally easy to install, provide excellent thermal performance, and are resistant to moisture and mold. Insulation boards are also lightweight, durable, and can be applied to various surfaces, including walls and floors.
Disadvantages of using insulation boards
Despite their many benefits, insulation boards have a few disadvantages. They tend to be more expensive compared to other insulation options, such as fiberglass or cellulose. Additionally, some insulation boards may emit volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during manufacturing or installation, which can negatively impact indoor air quality if not properly ventilated.
Commonly Used Insulation Materials Rigid foam insulation
Rigid foam insulation is a type of insulation material made from polystyrene, polyisocyanurate, or polyurethane. It is known for its high thermal resistance and can be used in both residential and commercial buildings. Rigid foam insulation boards are lightweight, easy to install, and provide excellent moisture resistance.
Polystyrene insulation
Polystyrene insulation, often referred to as EPS insulation, is an affordable and effective insulation material. It is commonly used in walls, roofs, and floors to provide thermal insulation and improve energy efficiency. Polystyrene insulation boards have a closed-cell structure, which enhances their insulating properties and makes them resistant to moisture.
Polyisocyanurate (PIR) insulation
Polyisocyanurate (PIR) insulation is a versatile and high-performance insulation material. It is typically used on roofs, walls, and floors, offering excellent thermal conductivity and fire resistance. PIR insulation boards have a closed-cell structure and are known for their exceptional thermal stability and insulation efficiency.
Applications of Home Insulation Boards Insulating roofs and attics
Insulation boards are commonly used to insulate roofs and attics. By installing insulation boards in these areas, heat loss and gain can be significantly reduced, improving energy efficiency and maintaining a comfortable living environment. Insulation boards provide a continuous layer of insulation that helps prevent thermal bridging and minimizes the risk of condensation.
Floor insulation
Insulating the floors of a home using insulation boards can help improve thermal comfort and reduce energy consumption. Insulation boards are placed beneath the floor surface to create a barrier that prevents heat transfer between the interior and the ground. This is particularly beneficial for homes with suspended floors or those located in colder climates.
Insulating external walls
Insulation boards are also commonly used to insulate external walls. By installing insulation boards on the exterior or interior of the walls, heat transfer can be minimized, reducing energy loss and improving overall energy efficiency. Insulating external walls not only helps maintain a comfortable indoor temperature but also enhances the structural integrity of the building.
Choosing the Best Type of Insulation Board Considerations for selecting insulation boards
When selecting insulation boards, it is important to consider factors such as thermal performance, moisture resistance, ease of installation, and cost. Additionally, the specific requirements of each application should be taken into account to ensure the chosen insulation boards meet the desired performance criteria.
Factors that affect the insulation performance
Several factors can affect the insulation performance of boards, including the thickness of the insulation, the quality of installation, and the presence of any gaps or voids. It is essential to follow manufacturer guidelines and industry best practices to ensure the insulation boards perform effectively and deliver the desired energy efficiency benefits.
Recommended thickness for different areas in a home
The recommended thickness of insulation boards can vary depending on the specific application and the local climate. As a general guideline, thicker insulation is typically required in colder climates to reduce heat loss. Local building codes and energy efficiency regulations should be consulted to determine the appropriate insulation thickness for different areas of a home.
Installation and Maintenance of Insulation Boards Proper installation techniques
Proper installation techniques are crucial to ensure the insulation boards perform optimally. This includes accurately measuring and cutting the boards, securely fastening them to the substrate, and sealing any gaps or joints to prevent air leaks. It is recommended to hire a professional insulation contractor for complex installations or consult installation guides provided by the manufacturers.
Tips for maintaining insulation boards
Insulation boards generally require minimal maintenance. However, it is important to regularly inspect the boards for any signs of damage, such as cracks or moisture intrusion, and promptly address any issues. Additionally, maintaining proper ventilation and preventing excessive humidity can help preserve the integrity and performance of the insulation boards over time.
Routine inspections and repairs
Regular inspections of the insulation boards are recommended to ensure they remain in good condition and continue to provide effective insulation. Inspections should include checking for any damage, gaps, or deterioration that may compromise the insulation performance. If any issues are identified, repairs should be carried out promptly to maintain the thermal efficiency of the building.
How to Install Insulation Boards Preparing for Insulation Installation
Prior to installing insulation boards, it is essential to prepare the area properly. This involves cleaning the surfaces, removing any obstructions, and ensuring the area is dry and free from moisture. It is also important to wear personal protective equipment, such as gloves and goggles, during the installation process.
Step-by-Step Guide to Installing Insulation Boards
- Measure and cut the insulation boards to fit the desired area.
- Apply adhesive to the back of the boards and press them firmly against the surface.
- Use screws or nails to secure the boards in place, if necessary.
- Fill any gaps or joints with sealant to prevent air leakage.
- Repeat the process until the entire area is insulated.
- Inspect the installation for any imperfections or gaps, and make necessary adjustments.
Common Mistakes to Avoid in Insulation Board Installation
While installing insulation boards, it is crucial to avoid common mistakes that could compromise the effectiveness of the insulation. Some common mistakes include improper fitting, insufficient adhesive application, inadequate sealing of gaps, and ignoring proper ventilation. Taking the time to ensure the correct installation will maximize the benefits of insulation.
Tips for Choosing the Best Insulation Boards Factors to Consider When Selecting Insulation Boards
When choosing insulation boards, it is essential to consider factors such as thermal efficiency, durability, fire resistance, moisture resistance, and overall insulation performance. Additionally, the specific requirements of the area to be insulated, as well as local building codes and regulations, should be taken into account.
Comparing R-Values of Insulation Boards
The R-value measures the thermal resistance of insulation materials. Higher R-values indicate better insulation performance. When comparing insulation boards, it is crucial to consider their R-values to ensure optimal thermal efficiency.
Understanding the Energy Efficiency of Insulation Boards
Insulation boards play a significant role in improving energy efficiency. By reducing heat transfer and minimizing the need for excessive heating or cooling, they contribute to lower energy consumption and reduced utility bills. Understanding the energy-saving potential of insulation boards will help you make an informed choice while selecting the right insulation for your home.
Our Range of Insulation Boards
Knauf Thermal Laminate-Insulated Plasterboard
Knauf Thermal Laminate - Insulated Plasterboard is an insulation board that combines traditional plasterboard with high-performance thermal insulation. It improves energy efficiency by reducing heat loss through walls and ceilings. Its advantages include excellent thermal performance, easy installation, fire resistance, sound insulation, and moisture resistance, making it a durable and long-lasting solution for buildings.
Celotex GA4000 - High-Performance PIR Insulation Board
Celotex GA4000 is a high-performance PIR insulation board made from polyisocyanurate foam (PIR). It offers excellent thermal insulation properties, preventing heat transfer and leading to energy savings. It is easy to install, fire-resistant, lightweight, and has good moisture resistance, making it suitable for various building applications.
Celotex Thermaclass Cavity Wall 21 - Cavity Wall Insulation Board
Celotex Thermaclass Cavity Wall 21 is a cavity wall insulation board made from high-performance rigid polyisocyanurate foam (PIR). It is designed to enhance the thermal performance of walls by reducing heat loss and improving energy efficiency. The board is installed within the cavity between the inner and outer wall layers, offering benefits such as lower heating costs and increased comfort. Its key properties include excellent compressive strength and resistance to moisture, ensuring long-term durability and preventing dampness issues.
Knauf XPS Laminate Plus - Insulated Plasterboard
Knauf XPS Laminate Plus is an insulated plasterboard that combines traditional plasterboard with high-quality extruded polystyrene (XPS) insulation. It offers enhanced thermal and sound insulation properties, reducing heat loss and creating a comfortable living or working environment. The installation is simple, and the board is fire-resistant, moisture-resistant, and durable, providing long-term insulation performance for buildings.
Celotex TB4000 - High-Performance PIR Insulation Board
Celotex TB4000 is a high-performance insulation board made from polyisocyanurate (PIR) foam, suitable for roofs, walls, and floors. It offers excellent thermal insulation, reducing heat loss and improving energy efficiency. Its high compressive strength allows for use in load-bearing applications. The installation is straightforward, and the board is fire-resistant, lightweight, and moisture-resistant, making it versatile and safe for various building applications.
Warmline EPS Insulated Plasterboard
Warmline EPS Insulated Plasterboard is a type of insulation board that combines the properties of EPS (Expanded Polystyrene) and plasterboard. It offers excellent thermal insulation and is easy to install. This board is commonly used for internal wall insulation.
Cemblock Cemplate - Fibre Cement Board
Cemblock Cemplate is a fibre cement board that is non-combustible and resistant to moisture. It provides effective insulation and can be used for both internal and external applications.
Xtratherm XT/PR - PIR Insulation Board
Xtratherm XT/PR is a PIR (Polyisocyanurate) insulation board known for its high thermal performance. It is lightweight and offers excellent moisture resistance. This type of board is commonly used for roof and wall insulation.
Cembloc Cembacker - Cement Tile Backer Board
Cembloc Cembacker is a cement-based board that is primarily used as a tile backer. It provides a stable and moisture-resistant surface for tiling in wet areas such as bathrooms and kitchens.
Knauf Sound Panel Acoustic Plasterboard with Tapered Edge -12.5mm
Knauf Sound Panel Acoustic Plasterboard is specifically designed to reduce noise transmission between rooms. It has excellent sound absorption properties, making it an ideal choice for soundproofing applications.
How do home insulation boards contribute to energy efficiency?
Home insulation boards are crucial for achieving energy efficiency in residential buildings. Here are some ways in which they contribute:
Minimize heat loss/gain through walls
Insulation boards act as a barrier against heat transfer through walls. They help maintain a comfortable temperature indoors by preventing heat from escaping during winters and blocking heat from entering during summers.
Reduce energy consumption
By minimizing heat loss or gain, insulation boards reduce the reliance on heating and cooling systems. This, in turn, leads to a significant reduction in energy consumption, resulting in lower carbon emissions.
Lower utility bills
Improved energy efficiency means less usage of heating and cooling appliances, leading to lower utility bills. Homeowners can enjoy long-term savings by installing effective insulation boards that reduce the need for constant temperature regulation.
What are the benefits of using home insulation boards?
Using home insulation boards offers several advantages, making them an excellent investment for homeowners. Let's explore the benefits:
Increased comfort and thermal stability
Insulation boards help create a comfortable living environment by maintaining consistent temperatures throughout the house. This reduces the reliance on heating or cooling systems and enhances thermal stability.
Improved indoor air quality
Insulation boards not only regulate temperature but also act as a barrier against moisture and condensation. This helps prevent the growth of mold and mildew, leading to improved indoor air quality.
Reduced noise transmission
Some insulation boards, like the Knauf Sound Panel Acoustic Plasterboard, provide excellent sound absorption properties. They help minimize noise transmission between rooms, ensuring a peaceful and quiet living space.
How to choose the right home insulation board for your needs?
Choosing the right home insulation board requires careful consideration of various factors. Here are some essential aspects to evaluate:
Consider the R-value
The R-value of an insulation board indicates its thermal resistance. Higher R-values offer better insulation performance. Assess the R-value requirements based on your location and climate to ensure optimal energy efficiency.
Evaluate the moisture resistance
Moisture resistance is crucial, especially for areas prone to high humidity or moisture. Look for insulation boards that have excellent moisture resistance properties to prevent water damage and mold growth.
Assess fire resistance capabilities
If fire safety is a concern, choose insulation boards that are fire-resistant. These boards are specially designed to slow down the spread of flames, providing valuable time for escape and minimizing property damage.
What are some common applications of home insulation boards?
Home insulation boards can be used in various parts of a house to achieve efficient thermal insulation. Some common applications include:
Walls insulation
Insulation boards can be installed on both interior and exterior walls to minimize heat loss or gain. This helps regulate indoor temperatures and reduce energy consumption.
Ceiling insulation
Installing insulation boards in the ceiling helps prevent heat from escaping through the roof. This is particularly beneficial during colder months, as it keeps the house warm and minimizes energy wastage.
Floor insulation
Floor insulation boards are used to provide thermal insulation from the ground. Insulating the floor helps maintain a comfortable temperature indoors and prevents heat loss through the floor surface.
Conclusion
By using high-quality home insulation boards, homeowners can effectively enhance the energy efficiency and comfort of their homes. With various types of insulation boards available, it is essential to understand the different materials and their applications to make an informed choice. Whether you are looking to reduce utility bills, increase thermal stability, or improve indoor air quality, investing in home insulation boards is a step towards creating a more energy-efficient and sustainable living space.
Q: What is thermal insulation, and why is it important?
A: Thermal insulation is the process of reducing heat transfer between two objects or spaces. It is important because it helps to regulate temperature and improve energy efficiency by reducing the need for heating and cooling.
Q: How does insulation work?
A: Insulation works by slowing down the transfer of heat. It traps air or uses materials with low thermal conductivity to create a barrier that prevents heat from passing through.
Q: What are the benefits of insulating a home?
A: Insulating a home offers several benefits, such as reducing energy bills, improving indoor comfort, reducing noise transmission, and enhancing energy efficiency.
Q: What are the different types of insulation boards available?
A: There are various types of insulation boards available, including PIR insulation boards, foam boards, polystyrene boards, and reflective insulation boards.
Q: What is the best type of insulation for a roof?
A: The best type of insulation for a roof depends on various factors such as budget, roof type, and insulation properties. Some popular options include foam board insulation, thermal insulation, and reflective insulation.
Q: What is loft insulation, and why is it important?
A: Loft insulation refers to insulating the space between the roof and the ceiling of a home. It is important because it helps to keep the warmth inside the house during winter and prevent heat from entering during summer.
Q: How can insulation boards be used?
A: Insulation boards can be used to insulate walls, roofs, floors, and other areas of a building. They can be easily installed and provide effective thermal insulation.
Q: What are the benefits of using insulation boards?
A: The benefits of using insulation boards include improved energy efficiency, reduced heat loss, enhanced thermal comfort, and reduced energy bills.
Q: Can insulation be installed on a flat roof?
A: Yes, insulation can be installed on a flat roof. There are different insulation systems available for flat roofs, such as rigid foam insulation and reflective insulation.
Q: What is reflective insulation?
A: Reflective insulation is a type of insulation that reflects radiant heat instead of absorbing it. It usually consists of a reflective surface facing airspace, which helps to block heat transfer.