Similar Categories
The Complete Guide to Passive Fire Protection in the UK
Passive fire protection (PFP) plays a critical role in safeguarding buildings across the UK by preventing the spread of fire and smoke. Unlike active fire systems that require action (such as sprinklers or alarms), passive fire protection systems work independently to compartmentalise fire and limit its movement throughout a building. This guide explains the purpose of passive fire protection, key components, and how it enhances overall fire safety strategies.
What is Passive Fire Protection?
Passive fire protection (PFP) refers to a group of systems and materials designed to stop fire from spreading and protect the structural integrity of buildings. These systems work by containing fire and smoke to specific areas, preventing fire from spreading throughout a building.
The Purpose of Passive Fire Protection
-
Fire Compartmentation – Divides buildings into fire-resistant compartments using fire walls, floors, and barriers.
-
Structural Protection – Protects the structure of the building to prevent collapse during a fire.
-
Limiting Fire Spread – Passive fire protection measures slow the spread of fire and smoke, providing more time for evacuation and emergency response.
-
Compliance with Regulations – Essential for meeting UK building regulations and ensuring occupant safety.
Difference Between Active and Passive Fire Protection
-
Active Fire Protection – Systems that require action, such as sprinkler systems, alarms, and fire hoses. These systems are triggered by a fire alarm or manual activation.
-
Passive Fire Protection – Works without action, using fire-resistant materials to contain fire. Examples include fire walls, fire doors, and fire retardant materials.
How Passive Fire Protection Systems Work
-
Compartmentalisation – Fire compartmentation prevents the spread of fire within a building by containing it to specific zones.
-
Fire-Resistant Materials – Fire rated walls, floors, and ceilings provide structural fire protection.
-
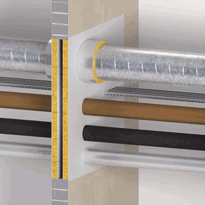
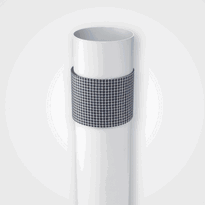
Fire Stopping Products – Seal gaps around pipes, ducts, and cables to prevent fire from spreading through voids.
-
Fire Resistance Ratings – PFP systems are tested to ensure they can withstand fire exposure for a specified period (e.g., 30, 60, 90 minutes).
Key Passive Fire Protection Measures
-
Fire Walls and Floors – Prevent fire from spreading between rooms and floors.
-
Fire Doors – Limit fire movement and protect escape routes.
-
Intumescent Coatings – Expand when exposed to heat, providing additional protection for structural steel and other materials.
-
Fire Dampers – Installed in ductwork to prevent fire and smoke from travelling through ventilation systems.
-
Cavity Barriers – Block the spread of fire through hidden spaces within walls and ceilings.
The Role of Passive Fire Protection in Fire Strategy
-
Fire Safety Strategy – PFP forms a key part of a comprehensive fire strategy, working alongside active fire protection to provide full coverage.
-
Risk Assessments – A thorough fire risk assessment should identify areas where passive fire protection solutions are needed.
-
Recommendations for Passive Fire Protection – Assessors provide recommendations to ensure fire risks are mitigated.
Examples of Passive Fire Protection Products
-
Rockwool Fire Barriers – Designed to provide fire compartmentation in large buildings.
-
Fire Rated Insulation Boards – Protect structural elements from fire exposure.
-
Intumescent Fire Seals – Expand to seal gaps in doors and joints.
Benefits of Passive Fire Protection
-
Slows the Spread of Fire – Provides essential time for evacuation.
-
Protects Structural Integrity – Reduces the risk of collapse during fire.
-
Non-Disruptive – Passive systems work silently in the background, requiring no activation.
-
Cost-Effective – Long-term solution for fire risk reduction without ongoing maintenance.
Conclusion
Passive fire protection is a vital part of any fire safety strategy. By implementing fire walls, fire compartmentation, and fire-resistant materials, property owners can reduce fire risk, protect occupants, and ensure compliance with UK fire regulations.
Invest in passive fire protection today to safeguard your building and provide peace of mind.